Guidelines for Billing and Medical Coding Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery, also known as Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) or Partial Knee Arthroplasty (PKA), involves replacing a damaged knee joint with an artificial prosthesis. Accurate medical coding and billing for knee replacement procedures are crucial for proper reimbursement and compliance with healthcare regulations. Below are the essential guidelines for coding and billing knee replacement procedures.
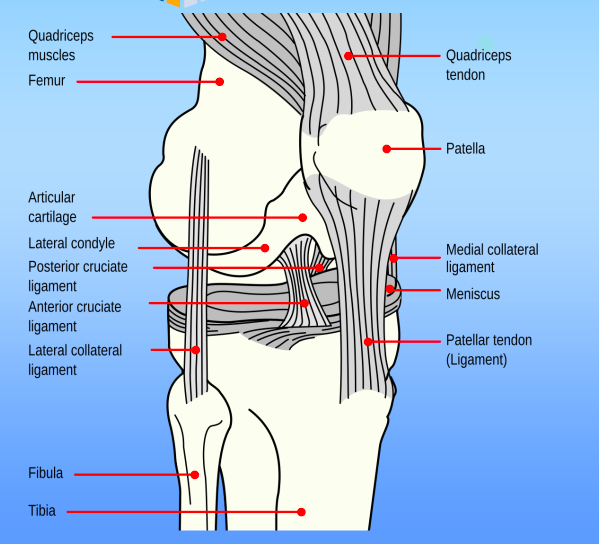
Knee Anatomy:
The medial compartment includes:
- Medial Femoral condyle
- Medial tibial plateau
- Medial meniscus
The lateral compartment includes:
- Lateral Femoral condyle
- Lateral tibial plateau
- Lateral meniscus
The Patellofemoral compartment includes:
- Patella
- Patellofemoral joint
- Intercondylar notch of the femur
- Suprapatellar pouch
- Trochlea
Understanding the Key Concepts
- Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA): The entire knee joint is replaced with a prosthesis, including the femoral, tibial, and patellar components.
- Partial Knee Arthroplasty (PKA): Only part of the knee joint is replaced (commonly one compartment such as medial or lateral).
- Revision Knee Surgery: A procedure that is performed to replace or repair an existing knee prosthesis that has failed, loosened, or become infected.
CPT Codes for Knee Replacement
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are used to report the specific type of knee replacement procedure performed. Common CPT codes for knee replacement surgeries include:
- Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA):
- 27447 – Total knee arthroplasty, with or without patellar resurfacing, unilateral.
- Partial Knee Arthroplasty (PKA):
- 27446 – Partial knee arthroplasty, medial or lateral compartment.
- Revision of Knee Arthroplasty:
- 27486 – Revision of total knee arthroplasty, with or without patellar resurfacing.
- Knee Arthroscopy (when performed in conjunction with TKA or PKA):
- 29870 – Arthroscopy, knee, diagnostic, with or without synovial biopsy.
- 29873 – Arthroscopy, knee, with meniscectomy (if performed in addition to replacement).
Note: If a knee arthroscopy is performed during the knee replacement to check for complications or assess the joint, ensure this is coded separately as an adjunct procedure. https://codingclarified.com/medical-coding-steps-for-cpt/
ICD-10 Codes for Diagnoses
ICD-10 codes are used to describe the diagnoses leading to the knee replacement. Common conditions resulting in knee replacement surgery include:
- Osteoarthritis (OA):
- M17.0 – Bilateral primary osteoarthritis of the knee.
- M17.1 – Unilateral primary osteoarthritis of the knee.
- Post-traumatic Osteoarthritis:
- M23.2 – Other derangements of the knee (due to prior trauma).
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
- M05.8x – Rheumatoid arthritis of the knee.
- Knee Pain:
- M25.561 – Pain in right knee.
- M25.562 – Pain in left knee.
- Other Conditions:
- M17.9 – Osteoarthritis of the knee, unspecified.
- M23.91 – Unspecified derangement of the knee.
Be sure to include the appropriate ICD-10 code(s) for the condition causing the need for the knee replacement, and any comorbidities that may impact the surgical outcome (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, obesity). https://codingclarified.com/medical-coding-steps-for-icd-10-cm/
Modifiers
Modifiers are used to provide additional information about the procedure performed. Common modifiers used for knee replacement surgeries include:
- Modifier 50 – Bilateral procedure. This modifier is used if the knee replacement is being performed on both knees.
- Modifier 59 – Distinct procedural service. This modifier should be used if multiple procedures are performed during the same operative session that are not typically bundled together (e.g., arthroscopy during TKA).
- Modifier 22 – Increased procedural services. This modifier may be used if the surgery requires more time or complexity than usual (e.g., revision surgeries). https://codingclarified.com/cpt-medical-modifiers/
Anesthesia Coding
Knee replacement surgeries are often performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia (spinal/epidural). The appropriate anesthesia CPT code should be used based on the anesthesia provided:
- Anesthesia for knee replacement:
- 01402 – Anesthesia for knee procedures, including total knee arthroplasty.
Ensure that the anesthesia provider accurately documents the anesthesia services and that appropriate modifiers (if applicable) are included.
Medical Coding Knee Replacement: Inpatient vs. Outpatient Billing
Knee replacement surgeries may be performed in either inpatient or outpatient settings, depending on the patient’s medical condition and the complexity of the procedure. The billing process for inpatient vs. outpatient care may differ in the following ways:
- Inpatient Billing (Facility):
- In an inpatient setting, the facility uses Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) codes for reimbursement.
- For TKA, a common DRG code could be DRG 469 (Major Joint Replacement or Reattachment of Lower Extremity with Major Complications or Comorbidities).
- Outpatient Billing (Facility):
- Outpatient facilities, including those utilizing Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) Billing Services will use Ambulatory Payment Classifications (APCs) and report the procedure using the appropriate outpatient CPT codes along with associated HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System) codes for any implants used.
- Physician Billing:
- Physicians use CPT codes for the surgical procedure (e.g., 27447 for TKA) and may also use specific codes for follow-up visits, including Evaluation and Management (E/M) codes for preoperative and postoperative care. https://codingclarified.com/choosing-between-outpatient-and-inpatient-medical-coding-which-path-is-right-for-you/
Implantable Device Coding (HCPCS Codes)
For billing purposes, knee replacement procedures that include the use of prosthetic implants require the use of HCPCS codes to identify the prosthetic devices. Common codes may include:
- L8610 – Knee prosthesis, metallic (without patellar component).
- L8612 – Patellar prosthesis (for total knee replacement).
- L8699 – Prosthetic device, not otherwise specified.
It’s essential to document the specific type of prosthetic implant used, as well as its model and serial number (if applicable) for insurance and patient records.
Medical Coding Knee Replacement: Documentation Requirements
To support correct coding and billing, thorough documentation of the procedure and patient condition is critical. Key documentation components include:
- Clear documentation of the preoperative diagnosis and operative procedure.
- Detailed notes on the type of knee replacement (total vs. partial) and any complications encountered.
- Records of any arthroscopic procedures or additional interventions (e.g., meniscectomy).
- Implant details such as the brand, model, and serial number of the prosthetic used.
- Postoperative diagnosis and patient condition.
Postoperative Care and Follow-Up
After knee replacement surgery, follow-up visits are often necessary. These visits are coded separately and should include the appropriate E/M codes based on the level of care provided. For example:
- 99211-99215 – Evaluation and management codes for follow-up visits.
Ensure that postoperative complications, such as infection or mechanical failure of the prosthesis, are documented accurately, as these may require additional visits or procedures that impact the coding and billing process.
Compliance and Auditing
To ensure compliance with regulations and to prevent improper billing or reimbursement delays, healthcare providers should:
- Regularly review the most recent CPT and ICD-10-CM/PCS updates.
- Implement strong internal auditing processes to verify that all codes are accurate and complete.
- Stay up-to-date with payer-specific requirements (e.g., Medicare, private insurers) regarding documentation and billing.
Proper coding and billing for knee replacement surgeries are essential for ensuring accurate reimbursement and compliance with regulatory standards. By adhering to these guidelines, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of claim denials or audits while maximizing reimbursement for the services provided. Always ensure that documentation is thorough, accurate, and supports the billed procedures and diagnoses.

