ICD-10-PCS (International Classification of Diseases, 10th Edition, Procedure Coding System) is used for coding inpatient procedures. Understanding the guidelines and tips for medical coding ICD-10-PCS is crucial for accurate coding and billing. Below are some important coding guidelines and helpful tips for medical coders:
ICD-10-PCS Coding Guidelines
Understand the Structure of ICD-10-PCS:
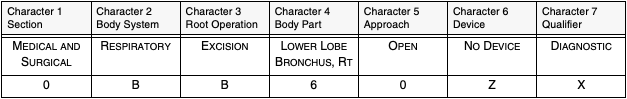
ICD-10-PCS codes are 7 characters long. Each character in the code represents a specific aspect of the procedure:
Character 1: Section (e.g., medical and surgical procedures, imaging)
Character 2: Body System (e.g., digestive system, musculoskeletal system)
Character 3: Root Operation (e.g., excision, insertion)
Character 4: Body Part (e.g., liver, pancreas)
Character 5: Approach (e.g., open, percutaneous)
Character 6: Device (e.g., prosthesis, stent)
Character 7: Qualifier (e.g., diagnostic, therapeutic)
Accurate Procedure Identification:
Make sure to identify the procedure accurately from the documentation in the medical record. Do not infer procedures that were not explicitly documented. If the procedure is not clearly documented, clarify with the physician or healthcare provider.
Coding Only Inpatient Procedures:
ICD-10-PCS is used for inpatient procedures only. For outpatient services, CPT codes are used instead. Ensure that the service provided qualifies as an inpatient procedure before applying ICD-10-PCS.
Root Operation Definitions:
A root operation is the main objective of the procedure. It is essential to understand the 31 root operations and their definitions. For example:
Extirpation: Removal of a solid mass from a body part
Resection: Removal of a portion of a body part
Drainage: Removal of fluid or gas from a body part
Division: Cutting or separation of a body part
Insertion: Placement of a device or material into a body part
Replacement: Substitution of a body part or device
Removal: Taking out a body part or device
Revision: Modification of an existing body part or device
Alteration: Changing the structure or function of a body part
Fusion: Joining two or more body parts together
Closure: Sealing a wound or opening
Destruction: Removal or inactivation of a body part or tissue
Transplantation: Transferring a body part from one person to another
Manipulation: Adjustment or repositioning of a body part
Measurement: Obtaining data on the size or function of a body part
Monitoring: Observing or tracking a body part or condition
Use of the Appropriately Described Body Part:
The body part code must reflect the actual site where the procedure was performed. For example, if a procedure was done on the left kidney, ensure you select the correct code for the left kidney.
Clarification of Device and Approach:
In cases where a device or an approach is used, document it clearly. For instance, if a procedure is performed using laparoscopic surgery (approach), make sure that is documented. Similarly, if a device is implanted, it should be coded.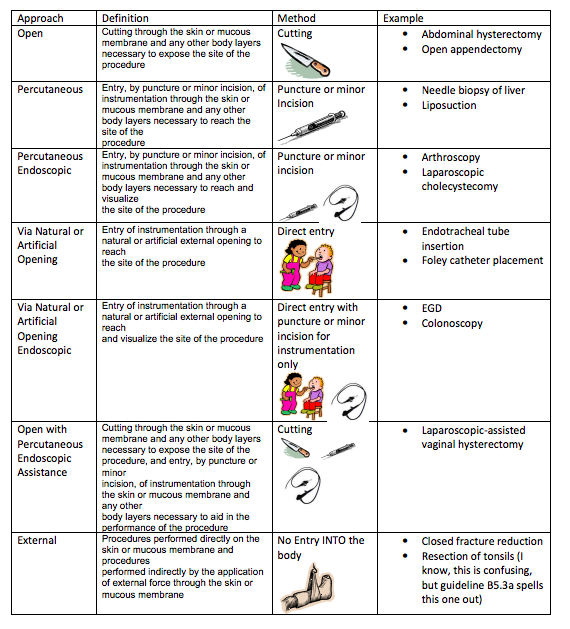
- Use of the Qualifier:
The qualifier, in the seventh character of ICD-10-PCS, can be used to indicate the nature of the procedure. For example, a diagnostic procedure versus a therapeutic procedure will have different qualifiers. This character is often overlooked but is important for accurate coding. - Coding Multiple Procedures:
If multiple procedures are performed during the same encounter, each procedure should be coded individually, even if they are related. Be sure to report all relevant procedures performed on the same day. - Look for Combination Codes:
Sometimes, a single code can describe multiple procedures (combination codes). Look for such codes when appropriate to avoid over-coding. - Avoid Upcoding:
Upcoding refers to reporting a higher-level procedure than what was actually performed. This is a form of fraudulent billing and can lead to serious penalties. Always ensure that the procedure code accurately reflects the service provided. Upcoding https://codingclarified.com/medical-coding-bundling-and-upcoding-guidelines/
ICD-10-PCS Coding Tips
- Review Documentation Thoroughly:
Always ensure that you are working with complete and accurate documentation. If the documentation is unclear or lacks detail, ask for clarification to prevent coding errors. - Use Coding Software/Reference Guides:
Utilize coding software or reference materials (e.g., ICD-10-PCS codebooks) to help guide your decision-making. These tools often have helpful search features and can provide insights into the most accurate codes. - Understand the Difference Between ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS:
ICD-10-CM (Clinical Modification) is used for diagnosis coding, while ICD-10-PCS is used for inpatient procedure coding. Make sure you’re using the correct system based on the situation. - Stay Updated:
ICD-10-PCS codes can change over time, with new codes added or existing codes modified. Keep up-to-date with the latest coding updates and revisions, which are often released annually (October 1st). - Collaborate with Physicians and Providers:
Clear communication with healthcare providers is essential. If there is ambiguity in the procedure description or if the documentation lacks certain details, don’t hesitate to reach out to the physician for clarification. - Check for Proper Code Sequencing:
When coding multiple procedures, ensure that they are sequenced in the correct order. This is especially important for procedures with different levels of complexity. Sequencing https://codingclarified.com/medical-coding-sequencing/?fbclid=IwZXh0bgNhZW0CMTAAAR3PoXB10L6bmKpLlik_ZYFCmi1RRtsqhaX72Ko-9oSTffXIcD6a6kmPNjE_aem_5KfXavENEz63gTJB316mDg - Utilize the ICD-10-PCS Table:
The ICD-10-PCS codebook has a “Table” format that can be incredibly helpful. This table allows you to drill down and choose the right characters for each part of the code. - Be Aware of Modifiers:
Unlike CPT, ICD-10-PCS does not use modifiers in the same way. However, sometimes the qualifier in the seventh character may act similarly by specifying additional information about the procedure. Medical Coding ICD-10 7th Character and Placeholder X https://codingclarified.com/medical-coding-icd-10-7th-character-and-placeholder-x/ - Focus on Compliance:
Ensure that your coding practices align with regulations such as HIPAA and Medicare guidelines to avoid audit issues. Incorrect coding can lead to claim denials, delays in payment, and even fines. - Review Payer-Specific Guidelines:
Be aware that some payers may have specific billing requirements or guidelines that differ slightly from the general ICD-10-PCS coding rules. Always check payer-specific instructions before submitting claims.
Accurate ICD-10-PCS coding and billing are crucial to ensuring proper reimbursement and compliance. A thorough understanding of the system, attention to detail in documentation, and clear communication with healthcare providers are essential for success in coding. Stay up-to-date with the latest coding changes and ensure all codes reflect the documented procedures appropriately.
ICD-10-PCS Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting 2025 https://www.cms.gov/files/document/2025-official-icd-10-pcs-coding-guidelines.pdf

