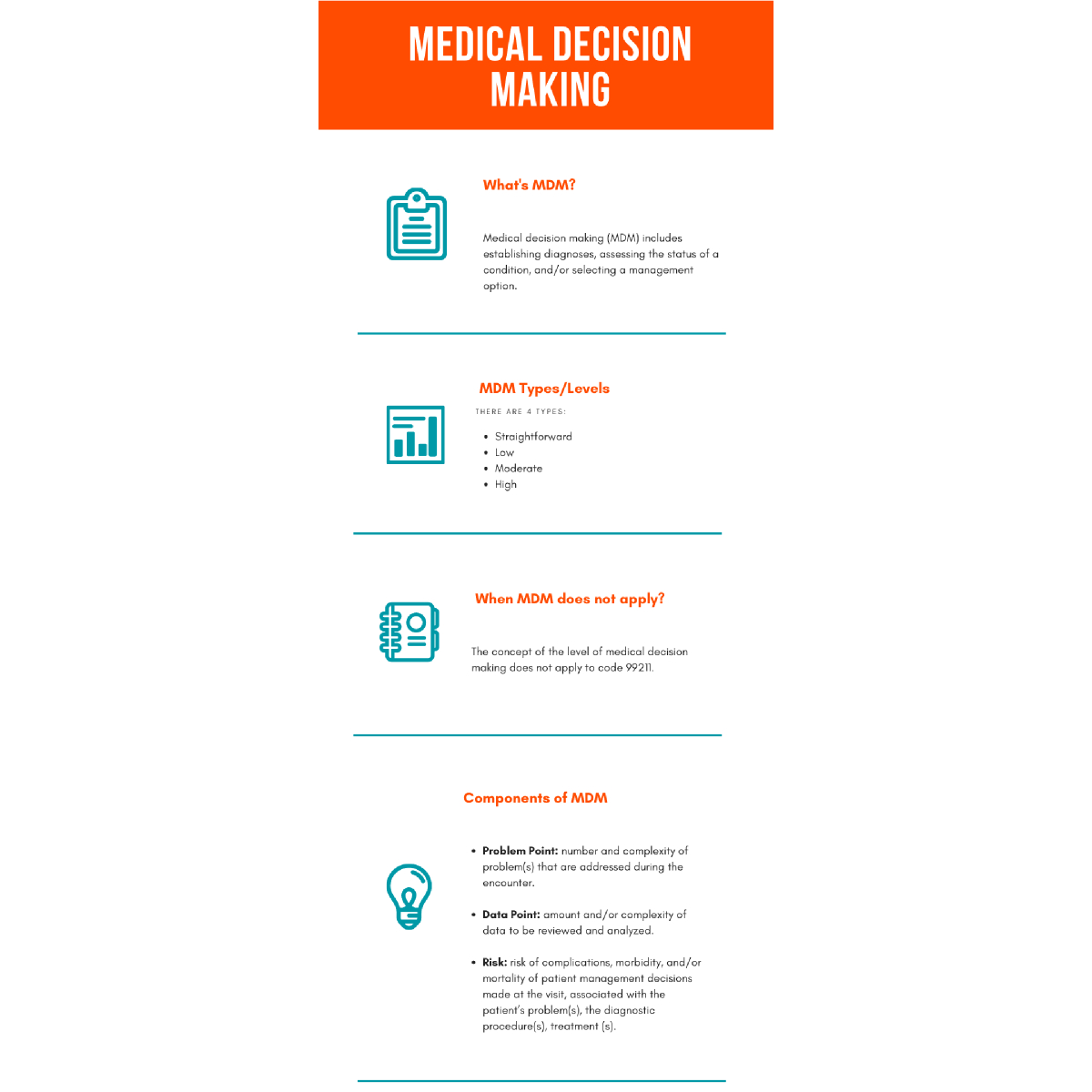
Medical Decision Making (MDM) is a core component of Evaluation and Management (E/M) services
It plays a significant role in determining the appropriate level of service to report for a patient encounter. As of the 2021 updates (and continuing into 2024-2025), the American Medical Association (AMA) and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) simplified the E/M coding guidelines for office and outpatient services to focus more on Medical coding MDM or time.
Here’s a detailed guide to Medical Decision Making (MDM) for coding and billing:
Understanding MDM: Key Components
MDM is determined by three elements:
-
Number and Complexity of Problems Addressed
-
Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed and Analyzed
-
Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity or Mortality of Patient Management
You must meet or exceed two out of three elements to support a particular MDM level.
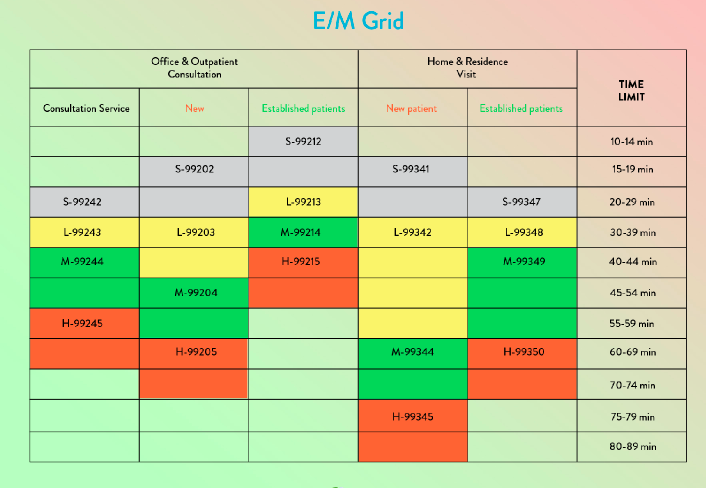
Levels of MDM
There are four levels of MDM:
| MDM Level | Problems Addressed | Data Reviewed | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Straightforward | 1 self-limited or minor problem | Minimal or none | Minimal risk of complications or morbidity |
| Low | 2+ self-limited/minor problems, or 1 stable chronic illness | Limited (e.g., 1 test or external note) | Low risk (e.g., OTC meds, minor procedures) |
| Moderate | 1+ chronic illness with exacerbation or 2+ stable chronic illnesses | Moderate (multiple tests, external notes, etc.) | Moderate (e.g., prescription drugs, minor surgery with risk) |
| High | 1+ chronic illnesses with severe exacerbation or acute illness posing threat to life/function | Extensive (e.g., independent interpretation, discussions with other professionals) | High (e.g., drug therapy requiring monitoring, decision to hospitalize) |
Element Details
Problems Addressed
A problem is “addressed” when it is actively evaluated, treated, or managed at the encounter.
-
Stable chronic illness is considered less complex than an exacerbated chronic illness or an acute problem with systemic symptoms.
Data Reviewed and Analyzed
Three types:
-
Category 1: Review/order of tests, notes, images, documents
-
Category 2: Independent interpretation of tests not separately reported
-
Category 3: Discussion with external healthcare professionals or family
- Use of decision aids, shared decision-making, and lab/imaging interpretation can support a higher MDM level.
Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity/Mortality
Includes:
-
Management decisions made (e.g., prescription, procedures)
- Risk of the condition if untreated
-
Nature of diagnostic/therapeutic interventions (e.g., elective surgery with identified risk factors)
Tips for Accurate MDM Coding
Document Clearly
-
-
Avoid ambiguous language. Be specific: “acute exacerbation” is stronger than “symptoms today.”
-
Note decision-making rationale even if no new tests or treatment is ordered.
Support Risk Appropriately
-
If prescribing meds, justify risk level (e.g., “start on anticoagulant due to atrial fibrillation”).
-
If recommending follow-up only, explain why that’s medically appropriate.
-
-
Avoid Overcoding or Undercoding
-
-
Don’t automatically assign higher MDM due to comorbidities unless they are addressed during the encounter.
-
A thorough history and exam do not affect MDM level under 2021+ guidelines — MDM or time determines code.
-
Use AMA MDM Grid
-
-
Use the official AMA grid for documentation and audit support.
-
Available in the CPT 2024 Professional Edition and AMA website.
-
Billing and Auditing Considerations
-
Time-based Coding (if used instead of MDM): Total time spent by provider on the date of service (face-to-face + non-face-to-face).
-
EHR Templates: Customize templates to prompt detailed documentation of MDM elements.
-
Audit Trail: Keep documentation that reflects your decision-making, particularly for high-risk situations.
Resources for Further Reading
Coding Clarified https://codingclarified.com/e-m-2025/
AMA CPT E/M Guidelines (2025) https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2023-e-m-descriptors-guidelines.pdf
CMS E/M Services Guide https://www.cms.gov/outreach-and-education/medicare-learning-network-mln/mlnproducts/downloads/eval-mgmt-serv-guide-icn006764.pdf
Interactive tools for E/M services