Medical Coding for Dialysis Guidelines
Dialysis is a life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), allowing them to maintain proper kidney function when their kidneys can no longer filter blood effectively. Accurate medical coding and billing for dialysis services is critical for healthcare providers to receive appropriate reimbursement from insurance payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers. This blog outlines the key guidelines for coding and billing dialysis treatments, including relevant codes, documentation requirements, and common billing challenges.
Overview of Dialysis
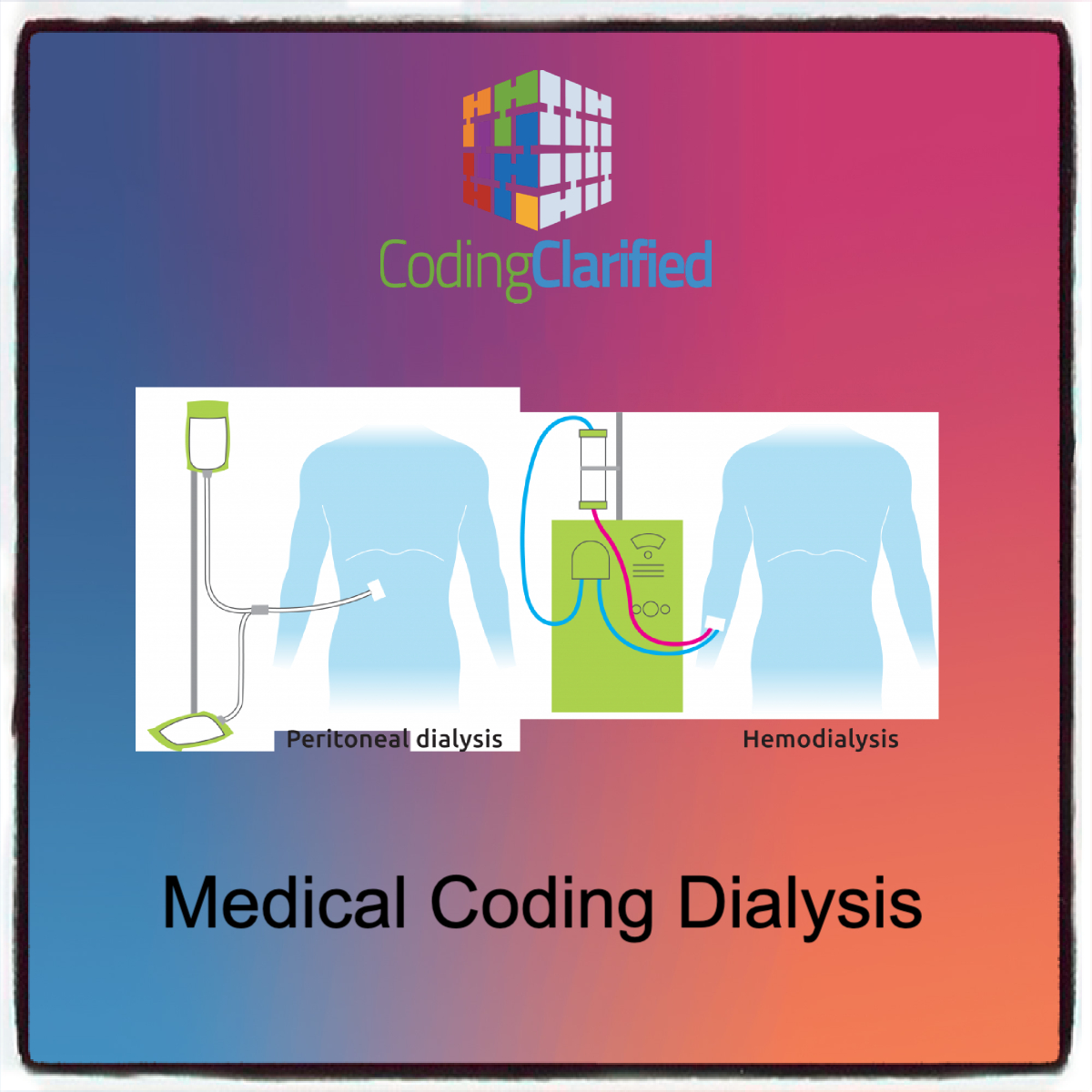
Dialysis comes in two primary forms:
- Hemodialysis (HD): A procedure where a machine filters waste, salt, and fluids from the blood. This is typically done in a dialysis center or at home with specialized equipment.
- Peritoneal Dialysis (PD): A procedure in which the lining of the abdomen (peritoneum) is used as a natural filter. It is typically done at home.
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes for Dialysis
The correct use of diagnosis codes is crucial for dialysis billing. The ICD-10-CM codes provide the foundation for documenting the condition that necessitates dialysis. The following are key codes associated with dialysis:
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): The majority of dialysis patients have CKD, which can range from stage 1 to stage 5. In the case of ESRD (end-stage renal disease), the code used is typically:
- N18.5 – End-stage renal disease
- N18.6 – Dialysis status (used for patients currently receiving dialysis)
- Other Relevant ICD-10 Codes:
- N18.3 – Chronic kidney disease, stage 3 (moderate)
- N18.4 – Chronic kidney disease, stage 4 (severe)
- I12.9 – Hypertensive heart AND chronic kidney disease, unspecified (for patients whose CKD is a result of hypertension)
- E11.22 – Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic nephropathy (for patients whose CKD is due to diabetes)
- Secondary Codes: Additional codes may be necessary to indicate the underlying condition causing ESRD, such as diabetes, hypertension, or other kidney diseases.
ICD steps to code https://codingclarified.com/medical-coding-steps-for-icd-10-cm/
CPT Medical Coding for Dialysis
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are used to report the specific services provided during dialysis treatments. The CPT codes vary depending on whether the patient is receiving hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis and whether the procedure is done in a facility or in the home setting.
CPT steps to code https://codingclarified.com/medical-coding-steps-for-cpt
Hemodialysis Codes (CPT 90935–90999):
- 90935 – Hemodialysis, including all components (can include physician oversight and direct care)
- 90937 – Hemodialysis, physician services (without supervision of the dialysis procedure itself)
- 90945 – Dialysis, peritoneal, including physician services
- 90947 – Dialysis, peritoneal, with physician supervision
- 90999 – Unlisted dialysis procedure (used when none of the listed codes apply)
Peritoneal Dialysis Codes:
- 90945 – Peritoneal dialysis, including physician services
- 90947 – Peritoneal dialysis, with physician supervision
- 90951 – Dialysis, peritoneal, catheter-related, each procedure
- 90952 – Dialysis, peritoneal, with catheter exchange
Modifiers for Dialysis
Modifiers provide additional information about the service provided. Commonly used modifiers for dialysis coding include:
- Modifier -25: Used to indicate that a significant, separately identifiable evaluation and management (E/M) service was provided on the same day as dialysis treatment.
- Modifier -59: Used when a procedure is performed separately from other procedures on the same day.
- Modifier -GT: Used to indicate telemedicine or telehealth services.
- Modifier -PO: Indicates that the dialysis service was provided in an outpatient setting.
CPT Medical Modifiers https://codingclarified.com/cpt-medical-modifiers/
Dialysis Treatment Time and Frequency
For hemodialysis, the frequency and duration of dialysis treatments must be documented accurately. Medicare guidelines typically require the patient to undergo hemodialysis three times a week for about 3-5 hours per session.
In-home dialysis settings, codes for home dialysis may include “training” and “management” components to ensure proper reimbursement for patient education and ongoing care. It’s essential that both the patient’s condition and the treatment modality (in-center vs. home dialysis) are clearly documented.
Medicare and ESRD Billing
Medicare provides comprehensive coverage for dialysis services for individuals with ESRD. The guidelines for billing dialysis services under Medicare include:
- ESRD Facility Services: Dialysis providers are reimbursed based on the Medicare ESRD Prospective Payment System (PPS), which includes payments for dialysis treatments, laboratory tests, drugs, and other services related to dialysis.Key billing codes under PPS include:
- Q4132–Q4136 for dialysis-related drugs
- PPS Base Rate (current year’s ESRD PPS rate for dialysis) applied according to the patient’s age, comorbidities, and location.
- Part B Coverage: Medicare Part B covers outpatient dialysis treatments, and claims must include the appropriate ICD-10 diagnosis code and CPT procedure code.
- Monthly Capitation Payment (MCP): Under the MCP model, providers receive a fixed payment for certain aspects of care that occur on a monthly basis, including physician services related to dialysis.
- Home Dialysis: Providers can also bill for home dialysis services, including home dialysis training and support, using specific CPT codes (e.g., 90989, 90993) and ensuring that home dialysis patients are monitored and managed appropriately.
- Drugs and Supplies: Medicare also covers certain dialysis-related drugs and supplies. Accurate coding for drugs administered during dialysis (e.g., erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, phosphate binders, etc.) is required. Providers should use HCPCS codes for these drugs (e.g., J0881 for erythropoiesis-stimulating agents).
Common Billing Errors in Dialysis
Dialysis billing can be complex, and there are common errors that providers need to avoid:
- Incorrect Diagnosis Coding: Ensure that the primary diagnosis (e.g., ESRD) is correctly coded and any secondary conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension) are included.
- Unbundling Services: Dialysis services should not be unbundled or separately billed unless specifically allowed by payer guidelines.
- Missing Documentation: Insufficient documentation to support the diagnosis, procedure, and treatment time can result in claim denials or reduced reimbursement.
- Improper Use of Modifiers: Incorrect or absent use of modifiers, especially when reporting services performed on the same day or in specific settings (e.g., home dialysis vs. facility), can lead to claim rejections.
- Inconsistent Reporting of Dialysis Frequency: Claims should match the patient’s treatment schedule, so discrepancies between billed codes and patient records (such as the frequency of dialysis sessions) can lead to denials.
Best Practices for Dialysis Billing
To ensure accurate and timely billing, healthcare providers should follow these best practices:
- Document Thoroughly: Ensure detailed documentation of the patient’s dialysis regimen, the frequency of treatments, and any complications or changes in condition.
- Verify Coding Accuracy: Use the most accurate and up-to-date ICD-10 and CPT codes, and verify that all applicable codes are used.
- Stay Informed on Payer Policies: Different payers (Medicare, Medicaid, private insurers) may have specific rules, so providers must stay updated on local payer policies and reimbursement rates.
- Utilize Professional Coders: Employ certified coders with expertise in nephrology and dialysis coding to ensure claims are processed correctly.
- Understand the ESRD PPS: Familiarize yourself with the Medicare ESRD Prospective Payment System to accurately report dialysis services and understand reimbursement rates.
Accurate coding and billing for dialysis services are critical for ensuring that healthcare providers are properly reimbursed for their care. Providers must stay informed on the latest coding guidelines, including the use of appropriate ICD-10 diagnosis codes, CPT codes for dialysis procedures, and modifiers. By following these guidelines, ensuring proper documentation, and addressing common billing challenges, dialysis providers can avoid claim denials and ensure timely payment for the essential services they provide to ESRD patients.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/14618-dialysis