2025 Guide to Evaluation and Management (E/M) Coding & Billing
The Evaluation and Management (E/M) coding system is used by healthcare providers to report and bill for services that involve patient evaluation and management. E/M coding plays a critical role in ensuring accurate reimbursement, improving compliance, and maintaining financial integrity for healthcare organizations.
In 2025, the American Medical Association (AMA) and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) have refined several aspects of E/M coding to align with the evolving healthcare landscape, simplifying certain processes while making others more precise.
Overview of E/M Codes
E/M codes fall under CPT codes (Current Procedural Terminology) and are used to describe the level of service provided during patient encounters. They are categorized by different factors, such as:
- Patient Type: New vs. Established
- Setting of Care: Office, hospital, or inpatient settings
- Complexity of the Encounter: Based on history, examination, and decision-making (MDM)
The key changes for 2025 focus on simplifying the coding structure for Evaluation and Management services, primarily by relying more on Medical Decision Making (MDM) than the previous system, which emphasized time and the extent of history and examination.
Key Evaluation and Management (E/M) Coding Changes for 2025
The 2025 changes to E/M coding bring more clarity to how healthcare providers should document and report their services. Here’s a breakdown of the important updates:
Medical Decision Making (MDM) Becomes the Primary Criterion
MDM now serves as the primary determinant for selecting the appropriate E/M level. This means that time and the extent of the history/examination are still relevant, but they are no longer the defining factors. In many cases, MDM will now determine the level of service.
- Level 1 (99202): Minimal/straightforward MDM
- Level 2 (99203): Low MDM
- Level 3 (99204): Moderate MDM
- Level 4 (99205): High MDM
History and Exam Requirements
For 2025, there is a shift from the detailed history and examination requirements to a more streamlined process. The focus is on whether the patient’s condition has a direct impact on the clinical decision-making process, rather than the length or depth of history taking and physical exam.
- History should be documented according to clinical necessity, but more emphasis is on medical decision-making.
- Comprehensive exams may be performed for complex cases, but they are no longer mandatory for certain levels of coding.
Updated MDM Scoring System
The MDM scoring system is now based on:
- Number and complexity of problems addressed
- Amount and complexity of data reviewed
- Risk of complications, morbidity, or mortality associated with the patient’s condition
The level of MDM determines the appropriate E/M code. MDM scoring aligns the code with the complexity of the provider’s decision-making process.
Evaluation and Management (E/M) Coding Guidelines for 2025
In order to select the correct E/M code, medical providers must assess the encounter based on the following key components:
- Patient History:
- Presenting Problem: Simple, self-limited conditions or complex, long-standing health concerns
- Past, Family, and Social History (PFSH): The degree of complexity (if relevant) will affect coding
- Review of Systems (ROS): Must align with clinical context
- Physical Examination:
- Based on the patient’s symptoms and complaint
- Detailed exams may be needed for more complicated issues
- Medical Decision Making (MDM):
- Major element in determining E/M level
- Based on diagnosis complexity and decision-making factors
- Considerations for diagnostic tests, patient referrals, and treatment options
E/M Codes for Office Visits (99202–99215)
- New Patient (99201-99205): For initial visits with a patient who has never been seen before.
- Established Patient (99211-99215): For follow-up visits where the patient has been seen in the last 3 years.
Oncologists Don’t Need to Watch the Clock to Document Time for E/M Codes: 3 Easy Tips
Tips for Accurate Evaluation and Management (E/M) Coding
Here are some essential tips for coding E/M services accurately in 2025:
Prioritize MDM Over History/Examination
Instead of focusing solely on the time spent with the patient or the details of the examination, carefully document the complexity of the decision-making process, which is the key to selecting the correct level.
Utilize Technology to Track MDM
Leverage electronic health records (EHR) and billing software to track MDM elements. Many systems now have automated tools that help determine the correct code based on your documentation, improving both efficiency and accuracy.
Be Aware of Updated Definitions
The definitions of the components of MDM can change year to year, so always review the most recent CPT guidelines. Ensuring the correct interpretation of these definitions is essential to avoid misreporting.
Ensure Consistency in Documentation
Consistency across the medical record is crucial. Each component, such as the history, exam, and medical decision-making, should align with one another and support the level of E/M service being claimed.
Use Code Modifiers Appropriately
Modifiers can adjust your claims based on unique circumstances of the encounter. Ensure modifiers are used according to the rules of CMS and the payer, to avoid denied claims.
E/M Billing Best Practices
Proper E/M billing practices are essential for healthcare practices to maximize revenue and minimize audit risk. Here are some of the best practices for E/M billing in 2025:
- Proper Documentation: Always ensure that documentation reflects the complexity of care and is sufficient to support the level of service reported. This can help prevent audits and claims denials.
- Understand Payer Guidelines: Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers may have varying rules and expectations for E/M codes, so be sure to check payer-specific requirements.
- Review and Correct Coding Before Submission: Double-check codes for accuracy before submission. Claims audits often find that billing errors are due to simple mistakes, such as incorrect code selection or failing to document properly.
- Follow Up on Claims: Ensure that submitted claims are followed up on promptly and that any discrepancies are resolved in a timely manner.
- Stay Current with Revisions: E/M codes are updated regularly. Stay current with annual revisions to CPT codes and CMS regulations to remain compliant.
Visual Aids for Evaluation and Management (E/M) Coding
Here are some helpful visual aids for understanding E/M coding for 2025:
MDM Scoring Levels
- Level 1 MDM: Minimal
- Level 2 MDM: Low
- Level 3 MDM: Moderate
- Level 4 MDM: Moderate to High
- Level 5 MDM: High
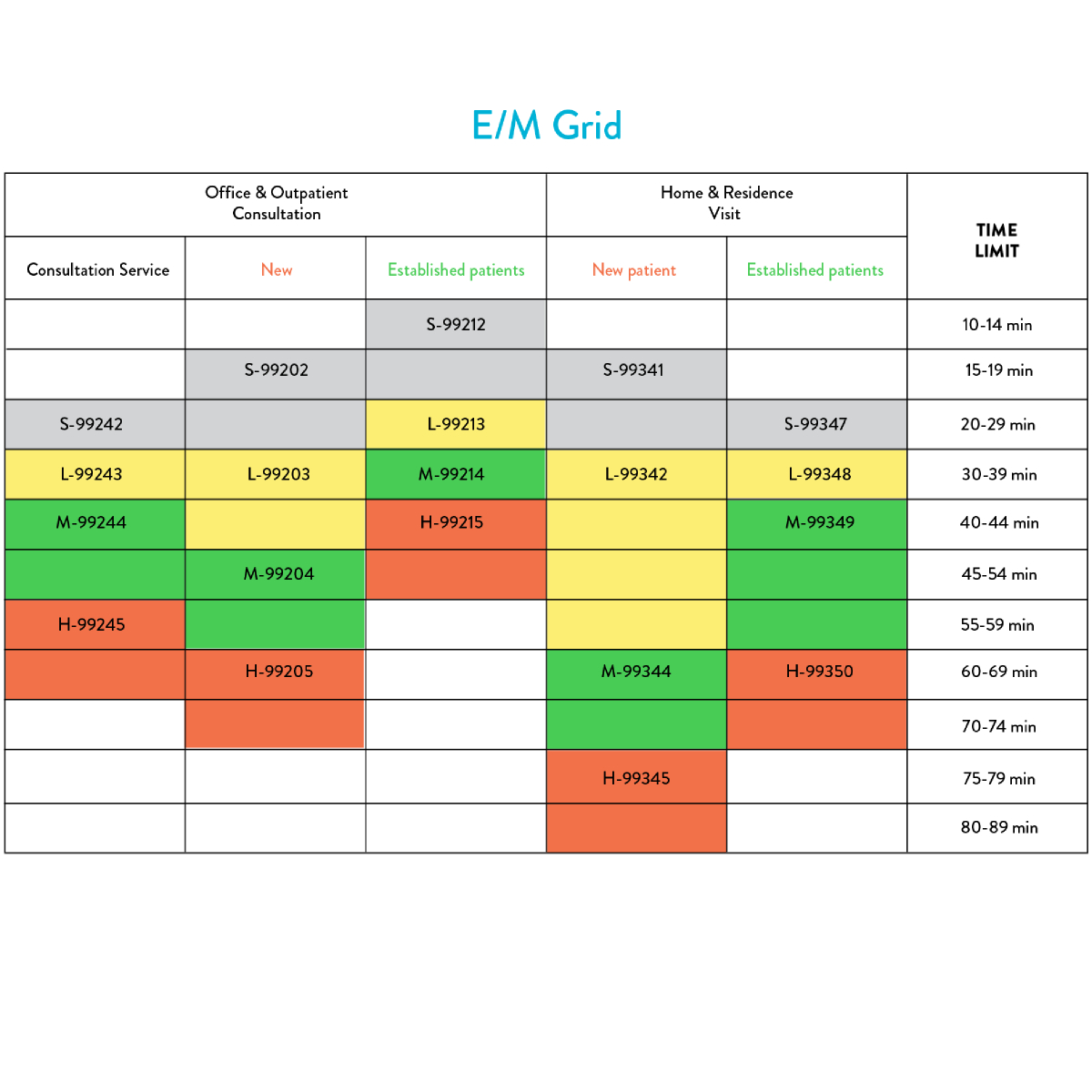
Code Selection Guide for Office Visits
- 99202–99205 for New Patients
- 99211–99215 for Established Patients
A simple comparison chart for new vs. established patient visits:
New Patient Established Patient|
99211 – Minimal
99202 – Low Complexity 99212 – Low
99203 – Moderate 99213 – Moderate
99204 – High Complexity 99214 – High
99205 – Highest Complexity 99215 – Highest
Effective E/M coding and billing are vital to ensuring the accurate compensation of healthcare services in 2025. By understanding the updates, particularly the shift to Medical Decision Making (MDM) as the primary determinant, and applying best practices for documentation and coding, healthcare providers can ensure compliance and efficiency.
Healthcare organizations should regularly train their staff, stay up-to-date with coding guidelines, and maintain a consistent focus on accuracy to navigate the complexities of E/M coding in 2025.
AMA E/M Resource https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2023-e-m-descriptors-guidelines.pdf

