Understanding Imaging Scans: Types, Coding, and Billing Guidelines
Imaging scans play a crucial role in modern medicine, enabling healthcare providers to diagnose and monitor a variety of conditions. Each type of imaging study has its own unique characteristics, applications, and associated coding guidelines. Understanding these can streamline the coding and billing processes, ensuring accurate reimbursement and compliance.
Types of Imaging Scans
- X-rays
- Description: X-rays use electromagnetic radiation to create images of bones and some tissues. They are often the first imaging study performed.
- Common Uses: Fractures, pneumonia, and dental issues.
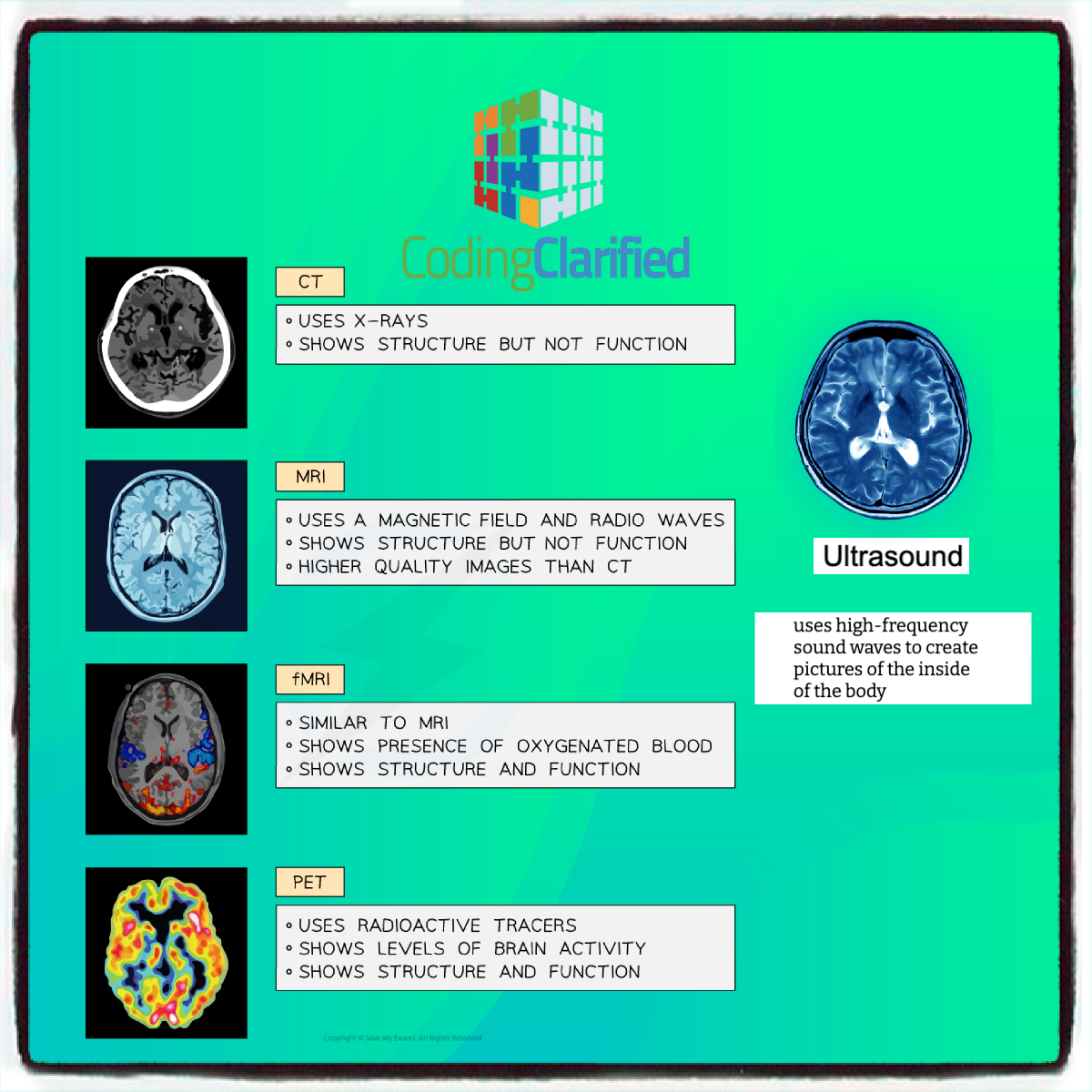
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
- Description: CT scans combine multiple X-ray images taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional views of bones and soft tissues.
- Common Uses: Tumor detection, internal bleeding, and organ injuries.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Description: MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of organs and tissues, particularly useful for soft tissues.
- Common Uses: Brain and spinal cord abnormalities, joint issues, and tumors.
- Ultrasound
- Description: Ultrasound employs high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs. It is non-invasive and does not use radiation.
- Common Uses: Pregnancy monitoring, organ examinations, and detecting fluid or masses.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans
- Description: PET scans use radioactive substances to visualize metabolic processes in the body, often combined with CT or MRI for more comprehensive imaging.
- Common Uses: Cancer detection and monitoring, brain disorders.
Coding Guidelines for Imaging Scans
Medical coding for imaging scans is guided by the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes.
CPT Coding
- X-rays: Typically coded using codes ranging from 70010 to 79999, depending on the area imaged.
- CT Scans: Codes generally fall within the range of 70450 to 70498, with specific codes for various body parts and contrast use.
- MRI: MRI codes range from 70551 to 70559, depending on the body part and whether it is performed with or without contrast.
- Ultrasound: Codes range from 76506 to 76999, with specific codes for various diagnostic procedures.
- PET Scans: PET codes typically fall between 78608 to 78609, depending on the type and location of the scan.
ICD Coding
ICD codes are used to indicate the reason for the imaging study. Accurate ICD coding ensures that the medical necessity for the imaging study is well-documented. Common examples include:
- Fractures: Use codes from the S codes (e.g., S02.9 for a fracture of the skull).
- Cancer Diagnosis: Use C codes for various types of cancer (e.g., C50.9 for breast cancer).
- Internal Bleeding: Codes from the R codes range (e.g., R58 for hemorrhage).
Billing Guidelines
- Documentation: Ensure that all imaging requests include pertinent clinical information, including symptoms, prior treatments, and the medical necessity of the imaging study.
- Modifiers: Use appropriate modifiers to indicate specific circumstances, such as bilateral procedures (modifier -50) or when the procedure is performed in an unusual manner (modifier -22).
- Global Period: Be aware of the global period associated with certain imaging studies, which may impact when subsequent services can be billed.
- Insurance Policies: Familiarize yourself with different insurance policies, as they may have specific requirements regarding prior authorization, coverage, and billing practices.
- Follow-Up Care: Ensure that any follow-up care resulting from the imaging study is appropriately coded and billed, linking it back to the original study when necessary.
Understanding the different types of imaging scans, along with their specific coding and billing guidelines, is essential for healthcare professionals involved in medical coding and billing. Accurate coding not only ensures appropriate reimbursement but also enhances patient care by facilitating timely diagnoses and treatment plans. By staying informed and organized, healthcare providers can navigate the complexities of imaging scans effectively.