Medical Coding Guide: The Female Reproductive System
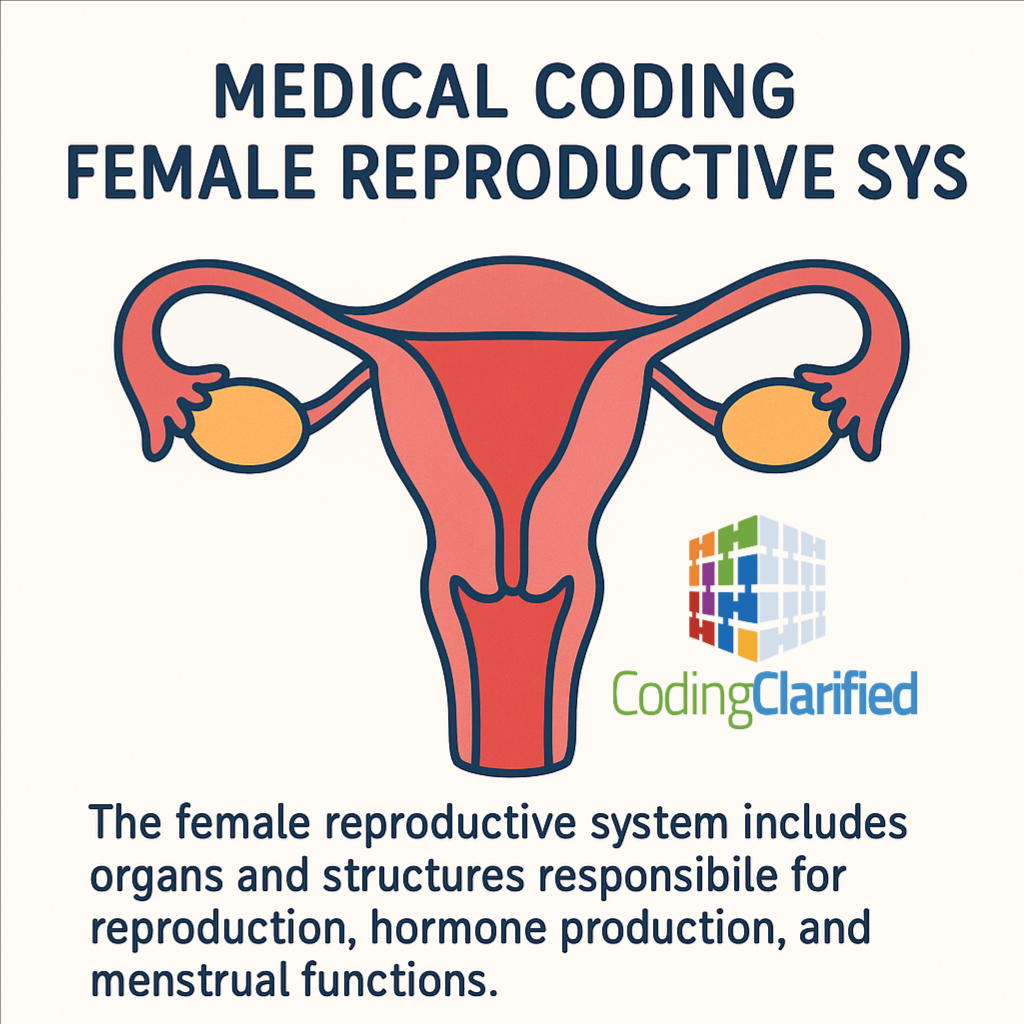
The female reproductive system includes organs and structures responsible for reproduction, hormone production, and menstrual functions. For medical coders, this body system is commonly seen in OB/GYN offices, hospitals, surgical settings, and preventive care visits. Accurate medical coding of the female reproductive system is essential for proper reimbursement and medical record compliance.
Key Organs in the Female Reproductive System
Understanding basic anatomy helps improve coding accuracy:
-
Ovaries – Produce eggs (ova) and hormones like estrogen and progesterone
-
Fallopian tubes – Transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus
-
Uterus – Where a fertilised egg implants and develops
-
Cervix – Lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina
-
Vagina – A Muscular canal that connects the cervix to the outside of the body
-
Vulva – External genital structures, including labia and clitoris
Common Diagnosis Coding (ICD-10-CM)
Female reproductive system conditions are primarily found in Chapter 14 (N00–N99).
Frequently used diagnosis categories include:
-
N80 – Endometriosis
-
N81 – Female genital prolapse
-
N83 – Noninflammatory disorders of the ovary, fallopian tube, and broad ligament
-
N84 – Polyps of the female genital tract
-
N85–N86 – Other disorders of the uterus and cervix
-
N92–N94 – Menstrual disorders and abnormal bleeding
-
N95 – Menopausal and perimenopausal disorders
Coding Tip
Always code to the highest level of specificity, including:
-
Laterality (right, left, bilateral when applicable)
-
Episode of care
-
Acute vs. chronic conditions
Common Procedure Coding (CPT®)
CPT codes for this system are mainly in the 58100–58999 range, along with evaluation and management and preventive codes.
Common CPT categories:
-
Pelvic exams
-
Pap smear procedures
-
Colposcopy and cervical biopsies
-
Endometrial biopsies
-
Hysteroscopy procedures
-
Laparoscopy of reproductive organs
-
Hysterectomy procedures
Coding Tip
Check documentation for:
-
Approach (open, laparoscopic, vaginal)
-
Extent of procedure (partial vs. total)
-
Whether any additional structures were removed
OB/GYN Preventive Services Coding
Preventive care is a major part of female reproductive system services.
Common codes include:
-
Well-woman exams (preventive E/M visits)
-
Pap smear collection and handling
-
Breast and pelvic exams
Helpful Guideline
Preventive services do not usually include management of existing conditions. If a problem-oriented service is significant and separately identifiable, you may need:
-
Modifier -25 appended to the E/M code
Important Medical Coding Guidelines
When coding the female reproductive system, follow these best practices:
-
Carefully review operative reports
-
Confirm the exact anatomical site involved
-
Code confirmed diagnoses, not “rule out” conditions (outpatient)
-
Use Z codes appropriately for routine gynaecological exams
-
Sequence primary diagnosis correctly based on reason for visit
Documentation Tips for Coders
Look for these key elements in provider documentation:
-
Reason for the visit
-
Symptoms and duration
-
Physical exam findings
-
Diagnostic test results
-
Postoperative diagnosis (for surgeries)
- Surgical approach: The method used for a procedure (abdominal, laparoscopic, transvaginal) must be accurately documented and coded.
- Procedure details: The coder must account for any additional procedures performed, such as a lymph node dissection or the removal of ovaries, and use the appropriate CPT codes.
Payer-Specific Tips
Different payers may have special rules for female reproductive services:
-
Some services are considered preventive and covered differently
-
Family planning services may require special modifiers or diagnosis codes
-
Global maternity packages have bundled services
Always verify coverage rules and medical necessity.
Accurate coding for the female reproductive system requires strong knowledge of anatomy, attention to clinical details, and careful application of ICD-10-CM and CPT® guidelines. Proper coding ensures clean claims, reduces denials, and supports high-quality patient care documentation
Spotlight on GYN Surgery Coding: An In-Depth Look at the CPT GYN Anatomy and Procedures Series