Medical Coding Deep Infiltrative Endometriosis (DIE): Guidelines & Tips
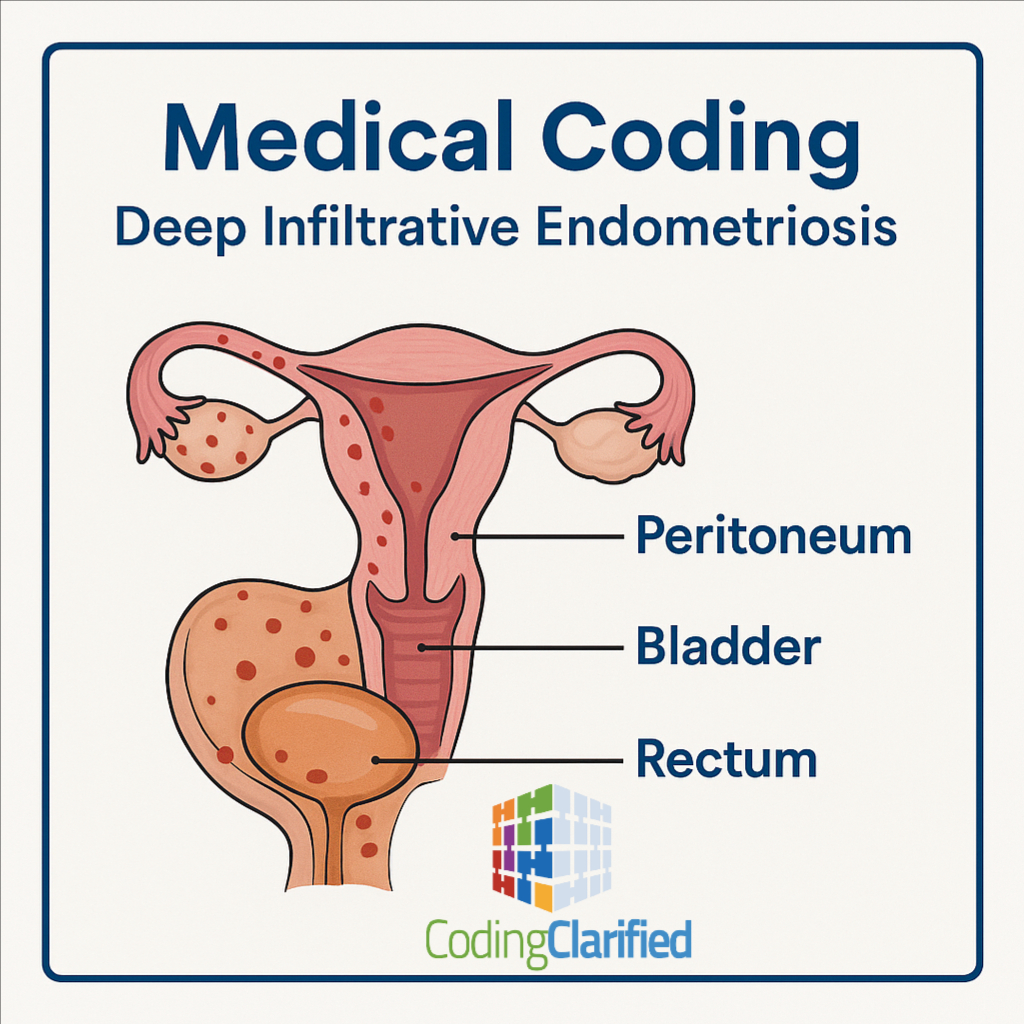
Deep infiltrative endometriosis (DIE) is a severe form of endometriosis where endometrial-like tissue penetrates more than 5 mm below the peritoneal surface. It often affects multiple pelvic structures — including the peritoneum, bladder, rectum, uterosacral ligaments, and bowel — and can cause chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and organ dysfunction. Here are some tips on medical coding Deep Infiltrative Endometriosis.
Because these lesions may span several anatomical sites, accurate ICD-10-CM coding requires careful review of the operative note and pathology report to identify all affected structures.
Commonly Involved Sites
-
Peritoneum – the most frequent location for DIE
-
Bladder – may cause urinary frequency, dysuria, or hematuria
-
Rectum or rectovaginal septum – often results in painful defecation
-
Uterosacral ligaments or cul-de-sac – associated with severe pelvic pain
-
Bowel or sigmoid colon – may mimic IBS symptoms
-
Vagina or cervix – less common but possible
ICD-10-CM Coding
Primary Codes
All endometriosis codes are found in Chapter 14 (N80) of ICD-10-CM.
Select the code based on the specific anatomic site(s) documented.
| ICD-10-CM Code | Description |
|---|---|
| N80.3 | Endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum |
| N80.4 | Endometriosis of the rectovaginal septum and vagina |
| N80.5 | Endometriosis of the intestine |
| N80.6 | Endometriosis in a cutaneous scar (post-surgical, e.g., cesarean) |
| N80.8 | Other endometriosis (e.g., bladder, ureter, etc.) |
| N80.9 | Endometriosis, unspecified |
Specific ICD-10-CM codes for DIE
- N80.02: Deep endometriosis of the uterus.
- N80.121: Deep endometriosis of the right ovary.
- N80.122: Deep endometriosis of the left ovary.
- N80.123: Deep endometriosis of bilateral ovaries.
- N80.129: Deep endometriosis of the ovary, unspecified ovary.
- N80.312: Deep endometriosis of the anterior cul-de-sac.
- N80.322: Deep endometriosis of the posterior cul-de-sac.
- N80.332: Deep endometriosis of the pelvic side wall.
- N80.4: Endometriosis of the rectovaginal septum and vagina.
- N80.5: Endometriosis of the intestines.
- N80.A: Endometriosis of the bladder and ureter.
- N80.B: Endometriosis of the cardiothoracic space.
- N80.C: Endometriosis of the abdomen.
- N80.D: Endometriosis of pelvic nerves.
- N80.8: Endometriosis of other sites.
If multiple sites are affected (e.g., peritoneum and rectum), assign multiple codes to capture each involved structure.
How to choose the correct DIE code
- Review the medical documentation: The coder must look for precise language in the surgeon’s or clinician’s notes that explicitly states “deep infiltrating,” “deep,” or “infiltrating” alongside the specific organ or tissue involved.
- Identify the location: Determine which organ or pelvic structure is affected by the DIE.
- Find the corresponding code: Navigate the ICD-10-CM table to find the N80 series and then select the code that specifies both the location and “deep” involvement.
- Confirm the specificity: Choose the most detailed and specific code available to accurately reflect the patient’s condition.
Documentation Tips
Accurate coding depends on detailed provider documentation. Encourage providers to specify:
-
Exact anatomic site(s) and depth of invasion
-
Laterality (if applicable)
-
Extent of organ involvement (e.g., partial vs. full-thickness bladder wall invasion)
-
Associated complications (obstruction, adhesions, infertility)
-
Procedural details if surgical excision or lysis of adhesions is performed
Surgical procedures
Coding Tips
-
Use multiple codes when more than one pelvic organ is involved.
Example:-
Endometriosis of the peritoneum (N80.3)
-
Endometriosis of intestine (N80.5)
-
Endometriosis of bladder (N80.8)
-
-
Do not default to N80.9 unless documentation is vague. Clarify with the provider before using “unspecified.”
-
Procedural coding (CPT) may be required for laparoscopic excision, fulguration, or resection. Examples include:
-
58662 – Laparoscopy, excision or destruction of lesions
-
58670 – Laparoscopy, fulguration of oviducts (sterilization, if performed)
-
49320 – Diagnostic laparoscopy (if only diagnostic)
-
-
Endometriosis of the bowel or urinary tract can also be clinically significant enough to require concurrent general surgery or urology codes — review operative notes carefully.
-
If infertility or pelvic pain is documented, consider coding the symptom or complication separately when appropriate (e.g., N97.9 Infertility, unspecified).
Example Coding Scenario
Operative Report:
Laparoscopic excision of deep infiltrative endometriosis involving the pelvic peritoneum, posterior bladder wall, and rectovaginal septum.
Codes:
-
N80.3 – Endometriosis of pelvic peritoneum
-
N80.8 – Endometriosis of the bladder
-
N80.4 – Endometriosis of rectovaginal septum and vagina
-
CPT 58662 – Laparoscopic excision or destruction of lesions
Key Takeaways
-
Always code to the deepest, most specific location identified.
-
Use multiple diagnosis codes when multiple pelvic organs are affected.
-
Encourage providers to document the extent of invasion (superficial vs. deep).
-
Cross-reference ICD-10-CM with CPT/HCPCS codes for procedures.
Understanding Deep Endometriosis: From Molecular to Neuropsychiatry Dimension
Historic Update to ICD-10 Endometriosis Diagnosis Codes
Coding Endometriosis With Improved Specificity
Medical Coding Blog