ICD-10-PCS (International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Procedure Coding System) is the system used in the United States to code inpatient hospital procedures. Unlike ICD-10-CM, which is used for diagnoses, ICD-10-PCS is specific to procedures performed in the hospital setting. Knowing how to build an ICD-10-PCS code requires a solid understanding of its structure and logic.
The Structure of an ICD-10-PCS Code
Every ICD-10-PCS code is seven characters long, and each character has a specific meaning:
- Section – Broad category of the procedure (e.g., Medical and Surgical, Obstetrics, Imaging).
- Body System – The general body system involved (e.g., cardiovascular, gastrointestinal).
- Root Operation – The objective of the procedure (e.g., excision, resection, insertion).
- Body Part – Specific anatomical site where the procedure is performed.
- Approach – How the procedure is performed (e.g., open, percutaneous, endoscopic).
- Device – Whether a device is left in place at the end of the procedure (e.g., stent, prosthesis).
- Qualifier – Provides additional information about the procedure (e.g., diagnostic vs. therapeutic).
How to Build an ICD-10-PCS Code
Identify the Procedure Section
- Example: Medical and Surgical procedures are always coded in Section 0.
- Imaging falls under Section B.
Determine the Body System
- Example: The heart and great vessels are in 2 (Cardiovascular system).
Define the Root Operation
- This is the most important step. The root operation describes the objective of the procedure:
- Excision – Cutting out a portion of a body part.
- Resection – Cutting out an entire body part.
- Insertion – Putting in a device.
- Bypass – Altering the route of contents of a tubular body part.
Specify the Body Part
- ICD-10-PCS identifies very specific locations.
- Example: Coronary artery, one site; Coronary artery, two sites, etc.
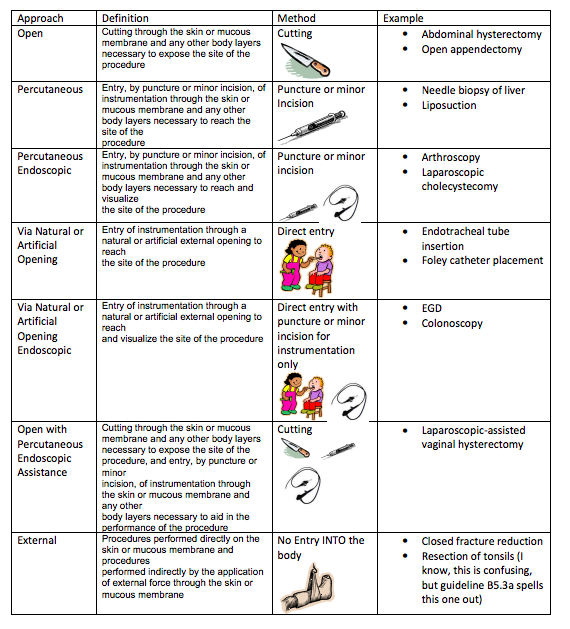
Select the Approach
- Defines how the procedure was performed:
- Open
- Percutaneous
- Percutaneous Endoscopic
- Via Natural or Artificial Opening
Identify the Device
- If a device is left in place, it must be captured.
- Example: Stent, pacemaker lead, prosthetic joint.
- If no device remains, this character is usually coded as Z (No device).
Assign the Qualifier
- Provides extra detail, often unique to the procedure.
- Example: “Diagnostic” qualifier if the procedure was done for testing purposes.
Example: Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Procedure: Aorto-coronary artery bypass with one site using autologous vein, open approach.
- Section (0): Medical and Surgical
- Body System (2): Heart and Great Vessels
- Root Operation (1): Bypass
- Body Part (0): Coronary Artery, One Site
- Approach (0): Open
- Device (9): Autologous Vein
- Qualifier (A): Aorta
Final Code: 021009A
Medical Coding CABG https://codingclarified.com/medical-coding-cabg/
Key Tips for Coders
- Always read the full operative report. Small details (approach, device, number of sites) change the code.
- Use the ICD-10-PCS Official Guidelines. They explain when to choose Excision vs. Resection, or how to assign multiple codes.
- Do not guess. PCS codes are very specific; if documentation is unclear, query the provider.
Bottom Line: ICD-10-PCS codes are built one character at a time, and each character represents a key piece of clinical information. Once you understand the structure, you can confidently construct accurate codes that reflect the procedure performed.
CMS Gov https://www.cms.gov/files/document/icd-10-pcs-2020-tables-and-index-pdf.pdf

